Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a rapidly growing field that aims to develop intelligent machines capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. Let us learn about the fundamental concepts of AI, explore its history and evolution, discuss its importance and various applications, and compare human intelligence with AI.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence, or AI, means making computers and machines think and act like humans. It helps machines learn new things, solve problems, understand what they see or hear, and even talk like people. The goal of AI is to create smart machines that can learn and improve by themselves, just like humans do.

History and Evolution of AI
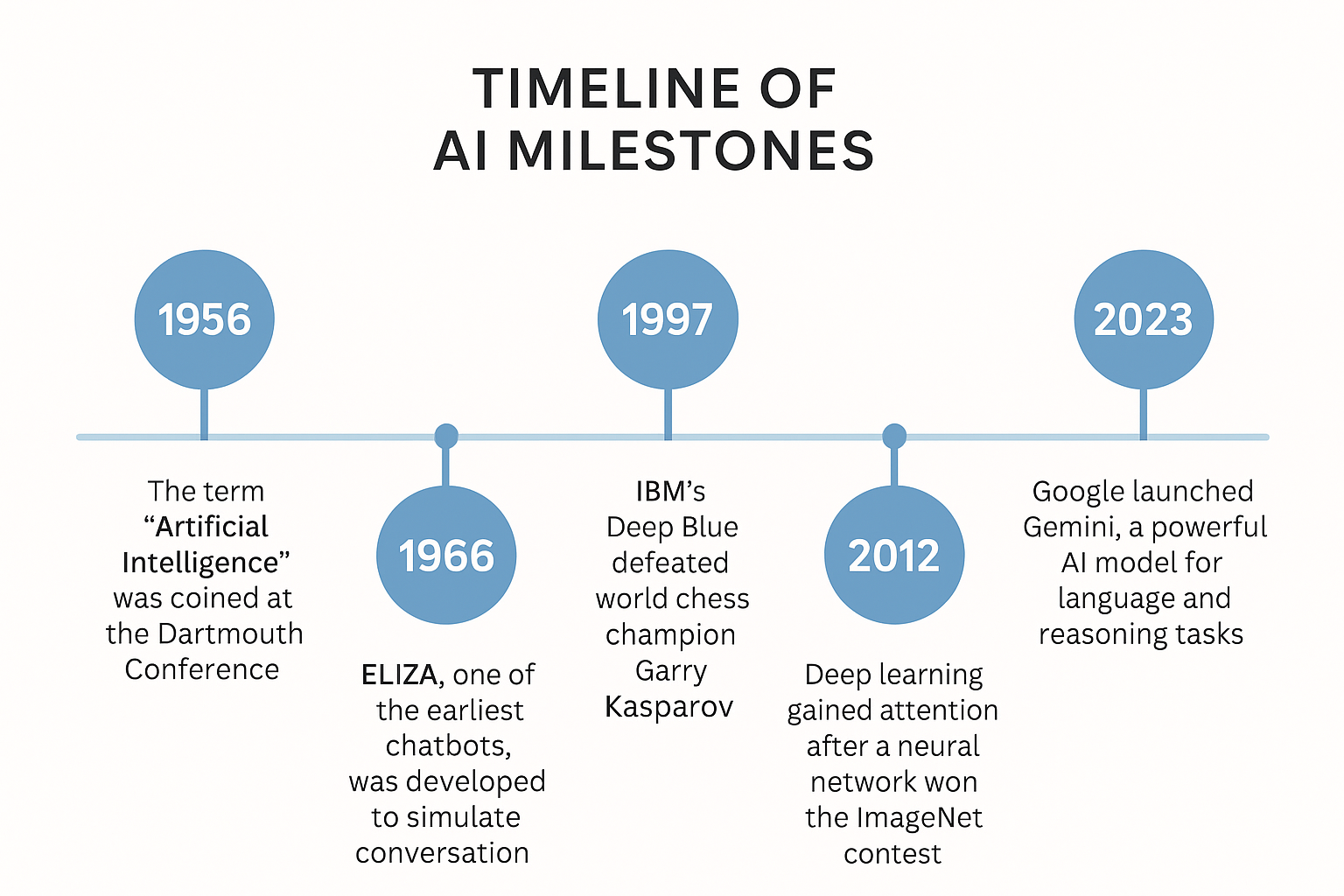
Early AI (1950s–1970s)
The history of AI began in the middle of the 1900s. In 1956, a scientist named John McCarthy and his team first used the term “artificial intelligence” at a meeting called the Dartmouth Conference. In the beginning, scientists worked on symbolic AI, where they used symbols and rules to help computers think. But progress was slow because computers were not very powerful, and it was hard to copy the way humans think. One famous example from that time was a chatbot called ELIZA.
Rise of Neural Networks (1980s–1990s)
In the 1980s and 1990s, there was a shift towards neural network-based methods (also popularly known as connectionist approaches) inspired by how the human brain works. This period saw significant advancements in:
- Machine Learning
- Pattern Recognition algorithms
- Expert Systems
- Natural Language Processing (NLP), and other AI applications.
For example: IBM’s Deep Blue, a chess-playing AI, became famous for defeating world champion Garry Kasparov in 1997.
Despite the progress, computing power and data availability were still limited during this period and neural networks were slow to train and not widely adopted in industry yet.
Modern AI and Deep Learning (2000s–present)
Fun Fact
Many AI programs are written in Python, a programming language named after the British comedy group Monty Python. Its simple syntax and powerful libraries make it a favorite among AI developers!
In the early 2000s, people became interested in AI again because of new progress in technology. One big improvement was deep learning, which is a way for computers to learn using special networks called neural networks. These networks have many layers and help computers do things like recognise pictures, understand speech, and even drive cars on their own. For example, AI tools like Google Translate and Google Gemini use deep learning to understand and create human language.
From rule-based logic to brain-inspired deep learning, AI has evolved rapidly and continues to transform the way machines interact with the world.
Importance and Applications of AI
AI has become increasingly important in today’s digital age, with various applications across various industries and domains. Some of the key areas where AI is making a significant impact include:
Making Work in Factories Faster and Better:
AI helps machines in factories work smoothly and fix problems before they break. For example, in car factories, AI robots can paint cars perfectly without any mistakes.
Helping Farmers Grow More Food:
AI tells farmers when to plant, water, and care for crops. Drones fly over the fields to check if plants are healthy. For example, AI sensors in the soil can tell farmers when to water their crops.
Producing Clean and Cheap Electricity:
AI helps control how electricity is made and used. It makes machines run better and saves energy. For example, AI controls wind turbines to make more electricity when the wind is strong.
Suggesting What to Watch or Listen To:
AI recommends movies, shows, or songs based on what you watched or listened to before. For example, Netflix uses AI to suggest shows you might enjoy.
Did You Know?
Netflix uses AI to save over $1 billion every year. Its smart recommendations keep people watching longer.
Helping Cars Drive Themselves:
AI helps self-driving cars see the road and decide when to turn, stop, or speed up. For example, Tesla’s Autopilot uses AI to drive safely without a driver.
Protecting Nature and the Planet:
AI checks forests, watches animals, and helps predict storms. For example, AI-powered drones help track wild animals and stop illegal hunting.
Keeping People Healthy:
Doctors use AI to find diseases early, choose treatments, and remind patients about medicines. For example, AI can study X-rays and MRIs to find signs of cancer.
Making Online Shopping Easier:
AI suggests products based on what you looked at or bought. This saves time and helps you find what you like. For example, Amazon shows you items based on your shopping history.

Helping Teachers and Students:
AI helps teachers understand how each student learns. It gives ideas to teach better and lets students learn at their own speed. For example, some learning apps use AI to give students activities based on their learning style.
Making Games and Movies More Fun:
AI helps make games, music, and movies more exciting. It creates smart characters in games, music playlists, and cool effects. For example, video games use AI to make characters behave like real people.
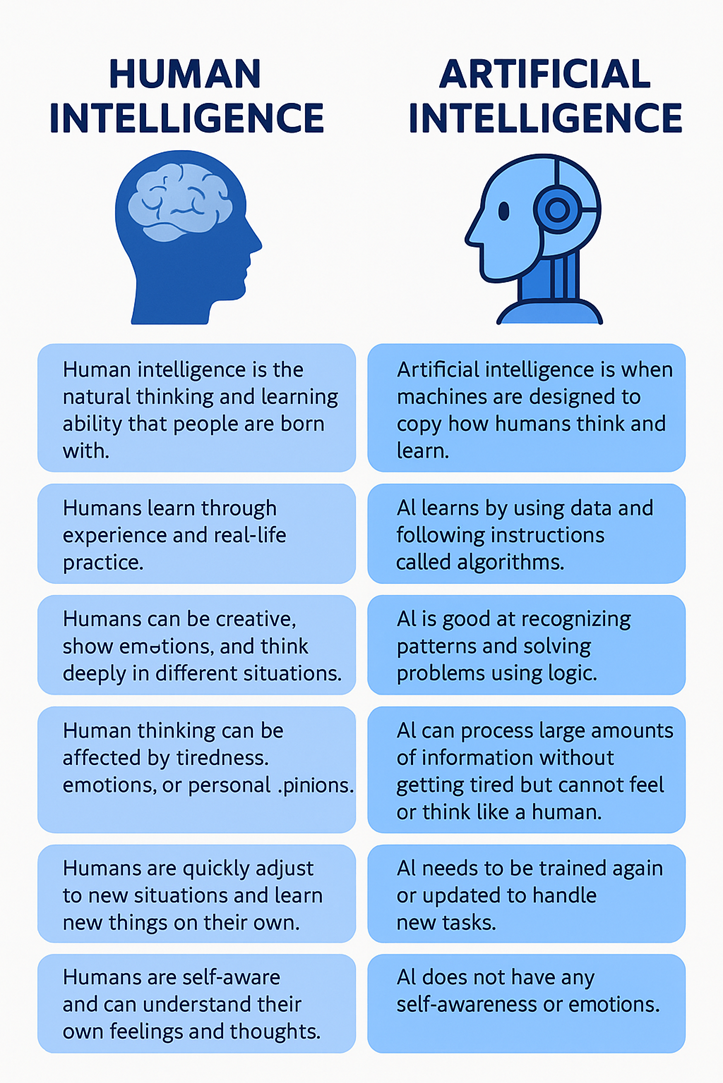
Human Intelligence vs. AI: A Comparison
Humans are very good at being creative, feeling emotions, and adjusting to new situations. On the other hand, AI is very good at handling large amounts of information and doing the same task over and over quickly and correctly. When humans and AI work together, they can solve big problems and bring new ideas in many fields.
Artificial Intelligence is changing the world around us. It is important for us to learn how it works, where it is used, and how to use it wisely. Additionally, it is necessary to be able to determine what is AI and what is not AI. When used responsibly, AI can make our lives easier, better, and more exciting.